Published - Tue, 06 Dec 2022

Networking Interview Questions and Answers
A list of top frequently asked networking interview questions and answers are given below
1) What is the network?
- A network is a set of devices that are connected with a physical media link. In a network, two or more nodes are connected by a physical link or two or more networks are connected by one or more nodes.
- A network is a collection of devices connected to each other to allow the sharing of data.
- Example of a network is an internet. An internet connects the millions of people across the world.
2) What do you mean by network topology?
Network topology specifies the layout of a computer network. It shows how devices and cables are connected to each other. The types of topologies are:
Bus:
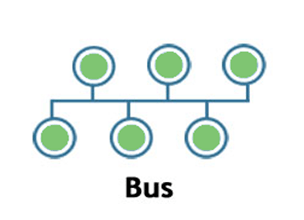
- Bus topology is a network topology in which all the nodes are connected to a single cable known as a central cable or bus.
- It acts as a shared communication medium, i.e., if any device wants to send the data to other devices, then it will send the data over the bus which in turn sends the data to all the attached devices.
- Bus topology is useful for a small number of devices. As if the bus is damaged then the whole network fails.
Star:
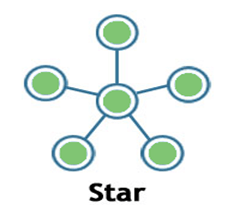
- Star topology is a network topology in which all the nodes are connected to a single device known as a central device.
- Star topology requires more cable compared to other topologies. Therefore, it is more robust as a failure in one cable will only disconnect a specific computer connected to this cable.
- If the central device is damaged, then the whole network fails.
- Star topology is very easy to install, manage and troubleshoot.
- Star topology is commonly used in office and home networks.
Ring
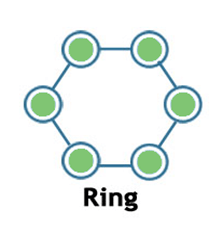
- Ring topology is a network topology in which nodes are exactly connected to two or more nodes and thus, forming a single continuous path for the transmission.
- It does not need any central server to control the connectivity among the nodes.
- If the single node is damaged, then the whole network fails.
- Ring topology is very rarely used as it is expensive, difficult to install and manage.
- Examples of Ring topology are SONET network, SDH network, etc.
Mesh
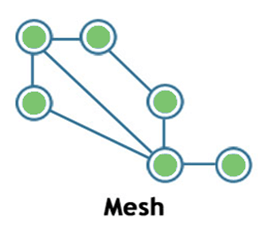
- Mesh topology is a network topology in which all the nodes are individually connected to other nodes.
- It does not need any central switch or hub to control the connectivity among the nodes.
- Mesh topology is categorized into two parts:
- Fully connected mesh topology: In this topology, all the nodes are connected to each other.
- Partially connected mesh topology: In this topology, all the nodes are not connected to each other.
- It is a robust as a failure in one cable will only disconnect the specified computer connected to this cable.
- Mesh topology is rarely used as installation and configuration are difficult when connectivity gets more.
- Cabling cost is high as it requires bulk wiring.
Tree
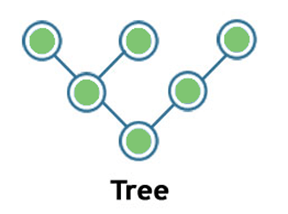
- Tree topology is a combination of star and bus topology. It is also known as the expanded star topology.
- In tree topology, all the star networks are connected to a single bus.
- Ethernet protocol is used in this topology.
- In this, the whole network is divided into segments known as star networks which can be easily maintained. If one segment is damaged, but there is no effect on other segments.
- Tree topology depends on the "main bus," and if it breaks, then the whole network gets damaged.
Hybrid
- A hybrid topology is a combination of different topologies to form a resulting topology.
- If star topology is connected with another star topology, then it remains star topology. If star topology is connected with different topology, then it becomes a Hybrid topology.
- It provides flexibility as it can be implemented in a different network environment.
- The weakness of a topology is ignored, and only strength will be taken into consideration.
3) What are the advantages of Distributed Processing?
A list of advantages of distributed processing:
- Secure
- Support Encapsulation
- Distributed database
- Faster Problem solving
- Security through redundancy
- Collaborative Processing
4) What is the criteria to check the network reliability?
Network reliability: Network reliability means the ability of the network to carry out the desired operation through a network such as communication through a network.
Network reliability plays a significant role in the network functionality. The network monitoring systems and devices are the essential requirements for making the network reliable.The network monitoring system identifies the problems that are occurred in the network while the network devices ensure that data should reach the appropriate destination.
The reliability of a network can be measured by the following factors:
- Downtime: The downtime is defined as the required time to recover.
- Failure Frequency: It is the frequency when it fails to work the way it is intended.
- Catastrophe: It indicates that the network has been attacked by some unexpected event such as fire, earthquake.
5) Which are the different factors that affect the security of a network?
There are mainly two security affecting factors:
- Unauthorized Access
- Viruses
6) Which are the different factors that affect the reliability of a network?
The following factors affect the reliability of a network:
- Frequency of failure
- Recovery time of a network after a failure
7) Which are the different factors that affect the performance of a network?
The following factors affect the performance of a network:
- Large number of users
- Transmission medium types
- Hardware
- Software
8) What makes a network effective and efficient?
There are mainly two criteria which make a network effective and efficient:
- Performance: : performance can be measured in many ways like transmit time and response time.
- Reliability: reliability is measured by frequency of failure.
- Robustness: robustness specifies the quality or condition of being strong and in good condition.
- Security: It specifies how to protect data from unauthorized access and viruses.
9) What is bandwidth?
Every signal has a limit of upper range frequency and lower range frequency. The range of limit of network between its upper and lower frequency is called bandwidth.
10) What is a node and link?
A network is a connection setup of two or more computers directly connected by some physical mediums like optical fiber or coaxial cable. This physical medium of connection is known as a link, and the computers that it is connected are known as nodes.
11) What is a gateway? Is there any difference between a gateway and router?
A node that is connected to two or more networks is commonly known as a gateway. It is also known as a router. It is used to forward messages from one network to another. Both the gateway and router regulate the traffic in the network.
Differences between gateway and router:
A router sends the data between two similar networks while gateway sends the data between two dissimilar networks.
12) What is DNS?
DNS is an acronym stands for Domain Name System.
- DNS was introduced by Paul Mockapetris and Jon Postel in 1983.
- It is a naming system for all the resources over the internet which includes physical nodes and applications. It is used to locate to resource easily over a network.
- DNS is an internet which maps the domain names to their associated IP addresses.
- Without DNS, users must know the IP address of the web page that you wanted to access.
Working of DNS:
If you want to visit the website of "javaTpoint", then the user will type "https://www.javatpoint.com" into the address bar of the web browser. Once the domain name is entered, then the domain name system will translate the domain name into the IP address which can be easily interpreted by the computer. Using the IP address, the computer can locate the web page requested by the user.
13) What is DNS forwarder?
- A forwarder is used with DNS server when it receives DNS queries that cannot be resolved quickly. So it forwards those requests to external DNS servers for resolution.
- A DNS server which is configured as a forwarder will behave differently than the DNS server which is not configured as a forwarder.
- Following are the ways that the DNS server behaves when it is configured as a forwarder:
- When the DNS server receives the query, then it resolves the query by using a cache.
- If the DNS server is not able to resolve the query, then it forwards the query to another DNS server.
- If the forwarder is not available, then it will try to resolve the query by using root hint.
14) What is NIC?
- NIC stands for Network Interface Card. It is a peripheral card attached to the PC to connect to a network. Every NIC has its own MAC address that identifies the PC on the network.
- It provides a wireless connection to a local area network.
- NICs were mainly used in desktop computers.
15) What is the meaning of 10Base-T?
It is used to specify data transfer rate. In 10Base-T, 10 specify the data transfer rate, i.e., 10Mbps. The word Base specifies the baseband as opposed to broadband. T specifies the type of the cable which is a twisted pair.
16) What is NOS in computer networking?
- NOS stands for Network Operating System. It is specialized software which is used to provide network connectivity to a computer to make communication possible with other computers and connected devices.
- NOS is the software which allows the device to communicate, share files with other devices.
- The first network operating system was Novel NetWare released in 1983. Some other examples of NOS are Windows 2000, Windows XP, Linux, etc.
17) What are the different types of networks?
Networks can be divided on the basis of area of distribution. For example:
- PAN (Personal Area Network): Its range limit is up to 10 meters. It is created for personal use. Generally, personal devices are connected to this network. For example computers, telephones, fax, printers, etc.
- LAN (Local Area Network): It is used for a small geographical location like office, hospital, school, etc.
- HAN (House Area Network): It is actually a LAN that is used within a house and used to connect homely devices like personal computers, phones, printers, etc.
- CAN (Campus Area Network): It is a connection of devices within a campus area which links to other departments of the organization within the same campus.
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): It is used to connect the devices which span to large cities like metropolitan cities over a wide geographical area.
- WAN (Wide Area Network): It is used over a wide geographical location that may range to connect cities and countries.
- GAN (Global Area Network): It uses satellites to connect devices over global are.
18) What is POP3?
POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol version3. POP is responsible for accessing the mail service on a client machine. POP3 works on two models such as Delete mode and Keep mode.
19) What do you understand by MAC address?
MAC stands for Media Access Control. It is the address of the device at the Media Access Control Layer of Network Architecture. It is a unique address means no two devices can have same MAC addresses.
20) What is IP address?
IP address is a unique 32 bit software address of a computer in a network system.
21) What is private IP address?
There are three ranges of IP addresses that have been reserved for IP addresses. They are not valid for use on the internet. If you want to access internet on these private IPs, you must have to use proxy server or NAT server.
22) What is public IP address?
A public IP address is an address taken by the Internet Service Provider which facilitates you to communication on the internet.
23) What is APIPA?
APIPA is an acronym stands for Automatic Private IP Addressing. This feature is generally found in Microsoft operating system.
24) What is the full form of ADS?
- ADS stands for Active Directory Structure.
- ADS is a microsoft technology used to manage the computers and other devices.
- ADS allows the network administrators to manage the domains, users and objects within the network.
- ADS consists of three main tiers:
- Domain: Users that use the same database will be grouped into a single domain.
- Tree: Multiple domains can be grouped into a single tree.
- Forest: Multiple trees can be grouped into a single forest.
25) What is RAID?
RAID is a method to provide Fault Tolerance by using multiple Hard Disc Drives.
26) What is anonymous FTP?
Anonymous FTP is used to grant users access to files in public servers. Users which are allowed access to data in these servers do not need to identify themselves, but instead log in as an anonymous guest.
27) What is protocol?
A protocol is a set of rules which is used to govern all the aspects of information communication.
28) What are the main elements of a protocol?
The main elements of a protocol are:
- Syntax: It specifies the structure or format of the data. It also specifies the order in which they are presented.
- Semantics: It specifies the meaning of each section of bits.
- Timing: Timing specifies two characteristics: When data should be sent and how fast it can be sent.
29 What is the Domain Name System?
There are two types of client/server programs. First is directly used by the users and the second supports application programs.
The Domain Name System is the second type supporting program that is used by other programs such as to find the IP address of an e-mail recipient.
30) What is link?
A link is connectivity between two devices which includes the cables and protocols used in order to make communication between devices.
31) How many layers are in OSI reference model?
OSI reference model: OSI reference model is an ISO standard which defines a networking framework for implementing the protocols in seven layers. These seven layers can be grouped into three categories:
- Network layer: Layer 1, Layer 2 and layer 3 are the network layers.
- Transport layer: Layer 4 is a transport layer.
- Application layer. Layer 5, Layer 6 and Layer 7 are the application layers.
There are 7 layers in the OSI reference model.
1. Physical Layer
- It is the lowest layer of the OSI reference model.
- It is used for the transmission of an unstructured raw bit stream over a physical medium.
- Physical layer transmits the data either in the form of electrical/optical or mechanical form.
- The physical layer is mainly used for the physical connection between the devices, and such physical connection can be made by using twisted-pair cable, fibre-optic or wireless transmission media.
2. DataLink Layer
- It is used for transferring the data from one node to another node.
- It receives the data from the network layer and converts the data into data frames and then attach the physical address to these frames which are sent to the physical layer.
- It enables the error-free transfer of data from one node to another node.
Functions of Data-link layer:
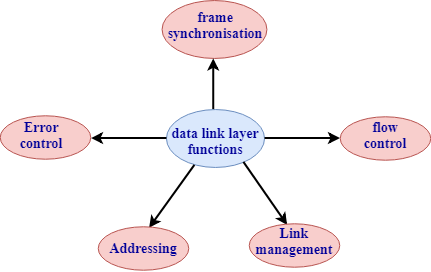
- Frame synchronization: Data-link layer converts the data into frames, and it ensures that the destination must recognize the starting and ending of each frame.
- Flow control: Data-link layer controls the data flow within the network.
- Error control: It detects and corrects the error occurred during the transmission from source to destination.
- Addressing: Data-link layer attach the physical address with the data frames so that the individual machines can be easily identified.
- Link management: Data-link layer manages the initiation, maintenance and, termination of the link between the source and destination for the effective exchange of data.
3. Network Layer
- Network layer converts the logical address into the physical address.
- It provides the routing concept means it determines the best route for the packet to travel from source to the destination.
Functions of network layer:
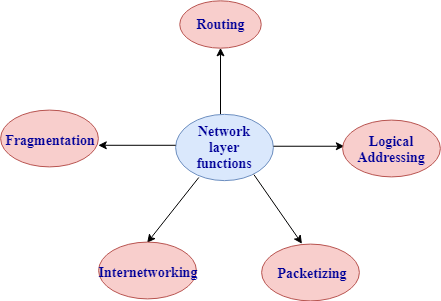
- Routing: The network layer determines the best route from source to destination. This function is known as routing.
- Logical addressing: The network layer defines the addressing scheme to identify each device uniquely.
- Packetizing: The network layer receives the data from the upper layer and converts the data into packets. This process is known as packetizing.
- Internetworking: The network layer provides the logical connection between the different types of networks for forming a bigger network.
- Fragmentation: It is a process of dividing the packets into the fragments.
4. Transport Layer
- It delivers the message through the network and provides error checking so that no error occurs during the transfer of data.
- It provides two kinds of services:
- Connection-oriented transmission: In this transmission, the receiver sends the acknowledgement to the sender after the packet has been received.
- Connectionless transmission: In this transmission, the receiver does not send the acknowledgement to the sender.
5. Session Layer
- The main responsibility of the session layer is beginning, maintaining and ending the communication between the devices.
- Session layer also reports the error coming from the upper layers.
- Session layer establishes and maintains the session between the two users.
6. Presentation Layer
- The presentation layer is also known as a Translation layer as it translates the data from one format to another format.
- At the sender side, this layer translates the data format used by the application layer to the common format and at the receiver side, this layer translates the common format into a format used by the application layer.
Functions of presentation layer:- Character code translation
- Data conversion
- Data compression
- Data encryption
7. Application Layer
- Application layer enables the user to access the network.
- It is the topmost layer of the OSI reference model.
- Application layer protocols are file transfer protocol, simple mail transfer protocol, domain name system, etc.
- The most widely used application protocol is HTTP(Hypertext transfer protocol ). A user sends the request for the web page using HTTP.
32) What is the usage of OSI physical layer?
The OSI physical layer is used to convert data bits into electrical signals and vice versa. On this layer, network devices and cable types are considered and setup.
33) Explain the functionality of OSI session layer?
OSI session layer provides the protocols and means for two devices on the network to communicate with each other by holding a session. This layer is responsible for setting up the session, managing information exchange during the session, and tear-down process upon termination of the session.
34) What is the maximum length allowed for a UTP cable?
The maximum length of UTP cable is 90 to 100 meters.
35) What is RIP?
- RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol. It is accessed by the routers to send data from one network to another.
- RIP is a dynamic protocol which is used to find the best route from source to the destination over a network by using the hop count algorithm.
- Routers use this protocol to exchange the network topology information.
- This protocol can be used by small or medium-sized networks.
36) What do you understand by TCP/IP?
TCP/IP is short for Transmission Control Protocol /Internet protocol. It is a set of protocol layers that is designed for exchanging data on different types of networks.
37) What is netstat?
The "netstat" is a command line utility program. It gives useful information about the current TCP/IP setting of a connection.
38) What do you understand by ping command?
The "ping" is a utility program that allows you to check the connectivity between the network devices. You can ping devices using its IP address or name.
39) What is Sneakernet?
Sneakernet is the earliest form of networking where the data is physically transported using removable media.
40) Explain the peer-peer process.
The processes on each machine that communicate at a given layer are called peer-peer process.
41) What is a congested switch?
A switch receives packets faster than the shared link. It can accommodate and stores in its memory, for an extended period of time, then the switch will eventually run out of buffer space, and some packets will have to be dropped. This state is called a congested state.
42) What is multiplexing in networking?
In Networking, multiplexing is the set of techniques that is used to allow the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals across a single data link.
43) What are the advantages of address sharing?
Address sharing provides security benefit instead of routing. That's because host PCs on the Internet can only see the public IP address of the external interface on the computer that provides address translation and not the private IP addresses on the internal network.
44) What is RSA Algorithm?
RSA is short for Rivest-Shamir-Adleman algorithm. It is mostly used for public key encryption.
45) How many layers are in TCP/IP?
There are basic 4 layers in TCP/IP:
- Application Layer
- Transport Layer
- Internet Layer
- Network Layer
46) What is the difference between TCP/IP model and the OSI model?
Following are the differences between the TCP/IP model and OSI model:
| TCP/IP model | OSI model |
|---|---|
| Full form of TCP is transmission control protocol. | Full form of OSI is Open System Interconnection. |
| TCP/IP has 4 layers. | OSI has 7 layers. |
| TCP/IP is more reliable than the OSI model. | OSI model is less reliable as compared to the TCP/IP model. |
| TCP/IP model uses horizontal approach. | OSI model uses vertical approach. |
| TCP/IP model uses both session and presentation layer in the application layer. | OSI Reference model uses separate session and presentation layers. |
| TCP/IP model developed the protocols first and then model. | OSI model developed the model first and then protocols. |
| In Network layer, TCP/IP model supports only connectionless communication. | In the Network layer, the OSI model supports both connection-oriented and connectionless communication. |
| TCP/IP model is a protocol dependent. | OSI model is a protocol independent. |
47) What is the difference between domain and workgroup?
| Workgroup | Domain |
|---|---|
| A workgroup is a peer-to-peer computer network. | A domain is a Client/Server network. |
| A Workgroup can consist of maximum 10 computers. | A domain can consist up to 2000 computers. |
| Every user can manage the resources individually on their PCs. | There is one administrator to administer the domain and its resources. |
| All the computers must be on the same local area network. | The computer can be on any network or anywhere in the world. |
| Each computer must be changed manually. | Any change made to the computer will reflect the changes to all the computers. |
Created by
Comments (0)
Search
Popular categories
IT Technical Interview
46common interview questions
18IT Multi National Company interview questions and Procedure
17Drug Related
8Pharmacy
7IQVIA interview questions and answers for Software jobs
5Latest blogs

General Aptitude
Fri, 16 Jun 2023

LabCorp Interview Questions & Answers:
Fri, 16 Jun 2023

HOW TO RESPOND TO BEHAVIORAL INTERVIEW QUESTIONS?
Fri, 16 Jun 2023


Write a public review