Published - Tue, 06 Dec 2022

Deep Learning Interview Questions and Answers
A list of top frequently asked Deep Learning Interview Questions and answers are given below.
1) What is deep learning?
Deep learning is a part of machine learning with an algorithm inspired by the structure and function of the brain, which is called an artificial neural network. In the mid-1960s, Alexey Grigorevich Ivakhnenko published the first general, while working on deep learning network. Deep learning is suited over a range of fields such as computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, etc.
2) What are the main differences between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
- AI stands for Artificial Intelligence. It is a technique which enables machines to mimic human behavior.
- Machine Learning is a subset of AI which uses statistical methods to enable machines to improve with experiences.

- Deep learning is a part of Machine learning, which makes the computation of multi-layer neural networks feasible. It takes advantage of neural networks to simulate human-like decision making.
3) Differentiate supervised and unsupervised deep learning procedures.
- Supervised learning is a system in which both input and desired output data are provided. Input and output data are labeled to provide a learning basis for future data processing.
- Unsupervised procedure does not need labeling information explicitly, and the operations can be carried out without the same. The common unsupervised learning method is cluster analysis. It is used for exploratory data analysis to find hidden patterns or grouping in data.
4) What are the applications of deep learning?
There are various applications of deep learning:
- Computer vision
- Natural language processing and pattern recognition
- Image recognition and processing
- Machine translation
- Sentiment analysis
- Question Answering system
- Object Classification and Detection
- Automatic Handwriting Generation
- Automatic Text Generation.
5) Do you think that deep network is better than a shallow one?
Both shallow and deep networks are good enough and capable of approximating any function. But for the same level of accuracy, deeper networks can be much more efficient in terms of computation and number of parameters. Deeper networks can create deep representations. At every layer, the network learns a new, more abstract representation of the input.
6) What do you mean by "overfitting"?
Overfitting is the most common issue which occurs in deep learning. It usually occurs when a deep learning algorithm apprehends the sound of specific data. It also appears when the particular algorithm is well suitable for the data and shows up when the algorithm or model represents high variance and low bias.
7) What is Backpropagation?
Backpropagation is a training algorithm which is used for multilayer neural networks. It transfers the error information from the end of the network to all the weights inside the network. It allows the efficient computation of the gradient.
Backpropagation can be divided into the following steps:
- It can forward propagation of training data through the network to generate output.
- It uses target value and output value to compute error derivative concerning output activations.
- It can backpropagate to compute the derivative of the error concerning output activations in the previous layer and continue for all hidden layers.
- It uses the previously calculated derivatives for output and all hidden layers to calculate the error derivative concerning weights.
- It updates the weights.
8) What is the function of the Fourier Transform in Deep Learning?
Fourier transform package is highly efficient for analyzing, maintaining, and managing a large databases. The software is created with a high-quality feature known as the special portrayal. One can effectively utilize it to generate real-time array data, which is extremely helpful for processing all categories of signals.
9) Describe the theory of autonomous form of deep learning in a few words.
There are several forms and categories available for the particular subject, but the autonomous pattern represents independent or unspecified mathematical bases which are free from any specific categorizer or formula.
10) What is the use of Deep learning in today's age, and how is it adding data scientists?
Deep learning has brought significant changes or revolution in the field of machine learning and data science. The concept of a complex neural network (CNN) is the main center of attention for data scientists. It is widely taken because of its advantages in performing next-level machine learning operations. The advantages of deep learning also include the process of clarifying and simplifying issues based on an algorithm due to its utmost flexible and adaptable nature. It is one of the rare procedures which allow the movement of data in independent pathways. Most of the data scientists are viewing this particular medium as an advanced additive and extended way to the existing process of machine learning and utilizing the same for solving complex day to day issues.
11) What are the deep learning frameworks or tools?
Deep learning frameworks or tools are:
Tensorflow, Keras, Chainer, Pytorch, Theano & Ecosystem, Caffe2, CNTK, DyNetGensim, DSSTNE, Gluon, Paddle, Mxnet, BigDL
12) What are the disadvantages of deep learning?
There are some disadvantages of deep learning, which are:
- Deep learning model takes longer time to execute the model. In some cases, it even takes several days to execute a single model depends on complexity.
- The deep learning model is not good for small data sets, and it fails here.
13) What is the meaning of term weight initialization in neural networks?
In neural networking, weight initialization is one of the essential factors. A bad weight initialization prevents a network from learning. On the other side, a good weight initialization helps in giving a quicker convergence and a better overall error. Biases can be initialized to zero. The standard rule for setting the weights is to be close to zero without being too small.
14) Explain Data Normalization.
Data normalization is an essential preprocessing step, which is used to rescale values to fit in a specific range. It assures better convergence during backpropagation. In general, data normalization boils down to subtracting the mean of each data point and dividing by its standard deviation.
15) Why is zero initialization not a good weight initialization process?
If the set of weights in the network is put to a zero, then all the neurons at each layer will start producing the same output and the same gradients during backpropagation.
As a result, the network cannot learn at all because there is no source of asymmetry between neurons. That is the reason why we need to add randomness to the weight initialization process.
16) What are the prerequisites for starting in Deep Learning?
There are some basic requirements for starting in Deep Learning, which are:
- Machine Learning
- Mathematics
- Python Programming
17) What are the supervised learning algorithms in Deep learning?
- Artificial neural network
- Convolution neural network
- Recurrent neural network
18) What are the unsupervised learning algorithms in Deep learning?
- Self Organizing Maps
- Deep belief networks (Boltzmann Machine)
- Auto Encoders
19) How many layers in the neural network?
- Input Layer
The input layer contains input neurons which send information to the hidden layer. - Hidden Layer
The hidden layer is used to send data to the output layer. - Output Layer
The data is made available at the output layer.
20) What is the use of the Activation function?
The activation function is used to introduce nonlinearity into the neural network so that it can learn more complex function. Without the Activation function, the neural network would be only able to learn function, which is a linear combination of its input data.
Activation function translates the inputs into outputs. The activation function is responsible for deciding whether a neuron should be activated or not. It makes the decision by calculating the weighted sum and further adding bias with it. The basic purpose of the activation function is to introduce non-linearity into the output of a neuron.
21) How many types of activation function are available?
- Binary Step
- Sigmoid
- Tanh
- ReLU
- Leaky ReLU
- Softmax
- Swish
22) What is a binary step function?
The binary step function is an activation function, which is usually based on a threshold. If the input value is above or below a particular threshold limit, the neuron is activated, then it sends the same signal to the next layer. This function does not allow multi-value outputs.
23) What is the sigmoid function?
The sigmoid activation function is also called the logistic function. It is traditionally a trendy activation function for neural networks. The input data to the function is transformed into a value between 0.0 and 1.0. Input values that are much larger than 1.0 are transformed to the value 1.0. Similarly, values that are much smaller than 0.0 are transformed into 0.0. The shape of the function for all possible inputs is an S-shape from zero up through 0.5 to 1.0. It was the default activation used on neural networks, in the early 1990s.
24) What is Tanh function?
The hyperbolic tangent function, also known as tanh for short, is a similar shaped nonlinear activation function. It provides output values between -1.0 and 1.0. Later in the 1990s and through the 2000s, this function was preferred over the sigmoid activation function as models. It was easier to train and often had better predictive performance.
25) What is ReLU function?
A node or unit which implements the activation function is referred to as a rectified linear activation unit or ReLU for short. Generally, networks that use the rectifier function for the hidden layers are referred to as rectified networks.
Adoption of ReLU may easily be considered one of the few milestones in the deep learning revolution.
26) What is the use of leaky ReLU function?
The Leaky ReLU (LReLU or LReL) manages the function to allow small negative values when the input is less than zero.
27) What is the softmax function?
The softmax function is used to calculate the probability distribution of the event over 'n' different events. One of the main advantages of using softmax is the output probabilities range. The range will be between 0 to 1, and the sum of all the probabilities will be equal to one. When the softmax function is used for multi-classification model, it returns the probabilities of each class, and the target class will have a high probability.
28) What is a Swish function?
Swish is a new, self-gated activation function. Researchers at Google discovered the Swish function. According to their paper, it performs better than ReLU with a similar level of computational efficiency.
29) What is the most used activation function?
Relu function is the most used activation function. It helps us to solve vanishing gradient problems.
30) Can Relu function be used in output layer?
No, Relu function has to be used in hidden layers.
31) In which layer softmax activation function used?
Softmax activation function has to be used in the output layer.
32) What do you understand by Autoencoder?
Autoencoder is an artificial neural network. It can learn representation for a set of data without any supervision. The network automatically learns by copying its input to the output; typically,internet representation consists of smaller dimensions than the input vector. As a result, they can learn efficient ways of representing the data. Autoencoder consists of two parts; an encoder tries to fit the inputs to the internal representation, and a decoder converts the internal state to the outputs.
33) What do you mean by Dropout?
Dropout is a cheap regulation technique used for reducing overfitting in neural networks. We randomly drop out a set of nodes at each training step. As a result, we create a different model for each training case, and all of these models share weights. It's a form of model averaging.
34) What do you understand by Tensors?
Tensors are nothing but a de facto for representing the data in deep learning. They are just multidimensional arrays, which allows us to represent the data having higher dimensions. In general, we deal with high dimensional data sets where dimensions refer to different features present in the data set.
35) What do you understand by Boltzmann Machine?
A Boltzmann machine (also known as stochastic Hopfield network with hidden units) is a type of recurrent neural network. In a Boltzmann machine, nodes make binary decisions with some bias. Boltzmann machines can be strung together to create more sophisticated systems such as deep belief networks. Boltzmann Machines can be used to optimize the solution to a problem.
Some important points about Boltzmann Machine-
- It uses a recurrent structure.
- It consists of stochastic neurons, which include one of the two possible states, either 1 or 0.
- The neurons present in this are either in an adaptive state (free state) or clamped state (frozen state).
- If we apply simulated annealing or discrete Hopfield network, then it would become a Boltzmann Machine.
36) What is Model Capacity?
The capacity of a deep learning neural network controls the scope of the types of mapping functions that it can learn. Model capacity can approximate any given function. When there is a higher model capacity, it means that the larger amount of information can be stored in the network.
37) What is the cost function?
A cost function describes us how well the neural network is performing with respect to its given training sample and the expected output. It may depend on variables such as weights and biases.It provides the performance of a neural network as a whole. In deep learning, our priority is to minimize the cost function. That's why we prefer to use the concept of gradient descent.
38) Explain gradient descent?
An optimization algorithm that is used to minimize some function by repeatedly moving in the direction of steepest descent as specified by the negative of the gradient is known as gradient descent. It's an iteration algorithm, in every iteration algorithm, we compute the gradient of a cost function, concerning each parameter and update the parameter of the function via the following formula:
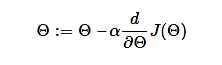
Where,
Θ - is the parameter vector,
α - learning rate,
J(Θ) - is a cost function
In machine learning, it is used to update the parameters of our model. Parameters represent the coefficients in linear regression and weights in neural networks.
39) Explain the following variant of Gradient Descent: Stochastic, Batch, and Mini-batch?
- Stochastic Gradient Descent
Stochastic gradient descent is used to calculate the gradient and update the parameters by using only a single training example. - Batch Gradient Descent
Batch gradient descent is used to calculate the gradients for the whole dataset and perform just one update at each iteration. - Mini-batch Gradient Descent
Mini-batch gradient descent is a variation of stochastic gradient descent. Instead of a single training example, mini-batch of samples is used. Mini-batch gradient descent is one of the most popular optimization algorithms.
40) What are the main benefits of Mini-batch Gradient Descent?
- It is computationally efficient compared to stochastic gradient descent.
- It improves generalization by finding flat minima.
- It improves convergence by using mini-batches. We can approximate the gradient of the entire training set, which might help to avoid local minima.
41) What is matrix element-wise multiplication? Explain with an example.
Element-wise matrix multiplication is used to take two matrices of the same dimensions. It further produces another combined matrix with the elements that are a product of corresponding elements of matrix a and b.
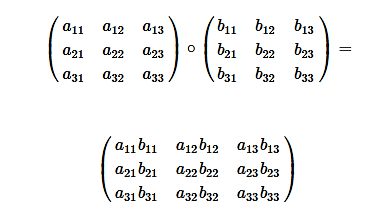
42) What do you understand by a convolutional neural network?
A convolutional neural network, often called CNN, is a feedforward neural network. It uses convolution in at least one of its layers. The convolutional layer contains a set of filter (kernels). This filter is sliding across the entire input image, computing the dot product between the weights of the filter and the input image. As a result of training, the network automatically learns filters that can detect specific features.
43) Explain the different layers of CNN.
There are four layered concepts that we should understand in CNN (Convolutional Neural Network):
- Convolution
This layer comprises of a set of independent filters. All these filters are initialized randomly. These filters then become our parameters which will be learned by the network subsequently. - ReLU
The ReLu layer is used with the convolutional layer. - Pooling
It reduces the spatial size of the representation to lower the number of parameters and computation in the network. This layer operates on each feature map independently. - Full Collectedness
Neurons in a completely connected layer have complete connections to all activations in the previous layer, as seen in regular Neural Networks. Their activations can be easily computed with a matrix multiplication followed by a bias offset.
44) What is an RNN?
RNN stands for Recurrent Neural Networks. These are the artificial neural networks which are designed to recognize patterns in sequences of data such as handwriting, text, the spoken word, genomes, and numerical time series data. RNN use backpropagation algorithm for training because of their internal memory. RNN can remember important things about the input they received, which enables them to be very precise in predicting what's coming next.
45) What are the issues faced while training in Recurrent Networks?
Recurrent Neural Network uses backpropagation algorithm for training, but it is applied on every timestamp. It is usually known as Back-propagation Through Time (BTT).
There are two significant issues with Back-propagation, such as:
- Vanishing Gradient
When we perform Back-propagation, the gradients tend to get smaller and smaller because we keep on moving backward in the Network. As a result, the neurons in the earlier layer learn very slowly if we compare it with the neurons in the later layers.Earlier layers are more valuable because they are responsible for learning and detecting simple patterns. They are the building blocks of the network.
If they provide improper or inaccurate results, then how can we expect the next layers and complete network to perform nicely and provide accurate results. The training procedure tales long, and the prediction accuracy of the model decreases. - Exploding Gradient
Exploding gradients are the main problem when large error gradients accumulate. They provide result in very large updates to neural network model weights during training.
Gradient Descent process works best when updates are small and controlled. When the magnitudes of the gradient accumulate, an unstable network is likely to occur. It can cause poor prediction of results or even a model that reports nothing useful.
46) Explain the importance of LSTM.
LSTM stands for Long short-term memory. It is an artificial RNN (Recurrent Neural Network) architecture, which is used in the field of deep learning. LSTM has feedback connections which makes it a "general purpose computer." It can process not only a single data point but also entire sequences of data.
They are a special kind of RNN which are capable of learning long-term dependencies.
47) What are the different layers of Autoencoders? Explain briefly.
An autoencoder contains three layers:
- Encoder
The encoder is used to compress the input into a latent space representation. It encodes the input images as a compressed representation in a reduced dimension. The compressed images are the distorted version of the original image. - Code
The code layer is used to represent the compressed input which is fed to the decoder. - Decoder
The decoder layer decodes the encoded image back to its original dimension. The decoded image is a reduced reconstruction of the original image. It is automatically reconstructed from the latent space representation.
48) What do you understand by Deep Autoencoders?
Deep Autoencoder is the extension of the simple Autoencoder. The first layer present in DeepAutoencoder is responsible for first-order functions in the raw input. The second layer is responsible for second-order functions corresponding to patterns in the appearance of first-order functions. Deeper layers which are available in the Deep Autoencoder tend to learn even high-order features.
A deep autoencoder is the combination of two, symmetrical deep-belief networks:
- First four or five shallow layers represent the encoding half.
- The other combination of four or five layers makes up the decoding half.
49) What are the three steps to developing the necessary assumption structure in Deep learning?
The procedure of developing an assumption structure involves three specific actions.
- The first step contains algorithm development. This particular process is lengthy.
- The second step contains algorithm analyzing, which represents the in-process methodology.
- The third step is about implementing the general algorithm in the final procedure. The entire framework is interlinked and required for throughout the process.
50) What do you understand by Perceptron? Also, explain its type.
A perceptron is a neural network unit (an artificial neuron) that does certain computations to detect features. It is an algorithm for supervised learning of binary classifiers. This algorithm is used to enable neurons to learn and processes elements in the training set one at a time.
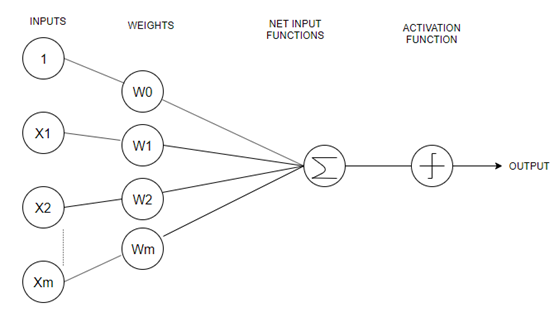
There are two types of perceptrons:
- Single-Layer Perceptron
Single layer perceptrons can learn only linearly separable patterns. - Multilayer Perceptrons
Multilayer perceptrons or feedforward neural networks with two or more layers have the higher processing power.
Created by
Comments (0)
Search
Popular categories
IT Technical Interview
46common interview questions
18IT Multi National Company interview questions and Procedure
17Drug Related
8Pharmacy
7Pharmacovigilance Interview Questions
5Latest blogs

General Aptitude
Fri, 16 Jun 2023

LabCorp Interview Questions & Answers:
Fri, 16 Jun 2023

HOW TO RESPOND TO BEHAVIORAL INTERVIEW QUESTIONS?
Fri, 16 Jun 2023


Write a public review